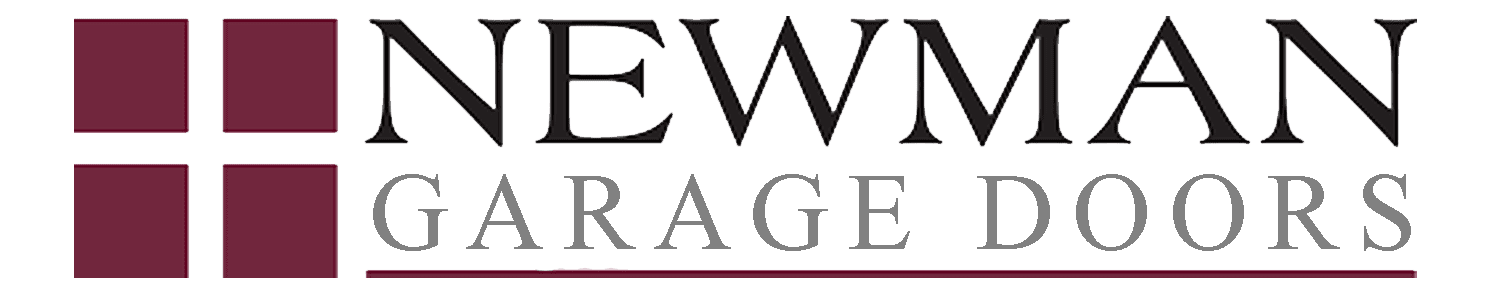Garage Door Services
Repairs | New Doors | Openers | Parts & Accessories
Garage Door Services: Professional Maintenance, Repair, and Installation Solutions
Modern residential and commercial properties rely on sophisticated automatic garage door systems that require professional maintenance and repair services. These complex mechanisms incorporate multiple components including motors, safety sensors, drive systems, and smart technology integration. When these systems malfunction, property owners require immediate access to qualified Garage Door Services that can diagnose and resolve issues efficiently, ensuring security and convenience remain uncompromised throughout the repair process.
The garage door service industry has evolved significantly with technological advancements in automation, wireless connectivity, and security features. Professional technicians must possess comprehensive knowledge of various drive mechanisms, electrical systems, circuit boards, and safety compliance requirements. Understanding the full spectrum of garage door opener components, repair methodologies, and preventative maintenance protocols enables service providers to deliver solutions that extend equipment lifespan while minimizing emergency repair situations and associated costs.
Garage Door Opener Types and Motor Drive Systems
The fundamental distinction between garage door opener systems lies in their drive mechanism configuration. Chain drive systems utilize a metal chain connected to a trolley that moves along a rail, providing reliable operation at an economical price point. These systems feature a gear and sprocket assembly powered by a motor, making them suitable for heavy residential doors. However, they generate considerable operational noise, which may be problematic for homes with living spaces adjacent to garage areas.
Belt drive systems represent a quieter alternative, employing a reinforced rubber drive belt instead of metal chains. These units deliver smooth, virtually silent operation ideal for attached garages beneath bedrooms or living areas. Screw drive mechanisms use a threaded steel rod that rotates to move the trolley carriage, offering fewer moving parts and reduced maintenance requirements. Direct drive systems feature the motor itself traveling along a stationary rail system, providing very quiet operation with minimal vibration transmission to mounting structures.
What Are the Power Requirements for Different Motor Types?
Residential garage door opener motors typically range from one-third horsepower to one horsepower, depending on door weight and size. Standard single-car doors generally require one-third to one-half horsepower units, while double-car doors and heavier materials necessitate three-quarter horsepower or greater. The power unit must generate sufficient torque to lift the door while maintaining proper force settings that prevent injury or damage when encountering obstructions during operation cycles.
Commercial applications often require industrial-grade motors exceeding one horsepower to accommodate frequent daily cycles and substantially heavier door constructions. These heavy-duty systems incorporate thermal overload protection preventing motor burnout during extended operation periods. Voltage requirements vary between standard 120-volt household circuits and dedicated 240-volt circuits for high-capacity commercial installations, with electrical wiring specifications determined by manufacturer guidelines and local building codes.
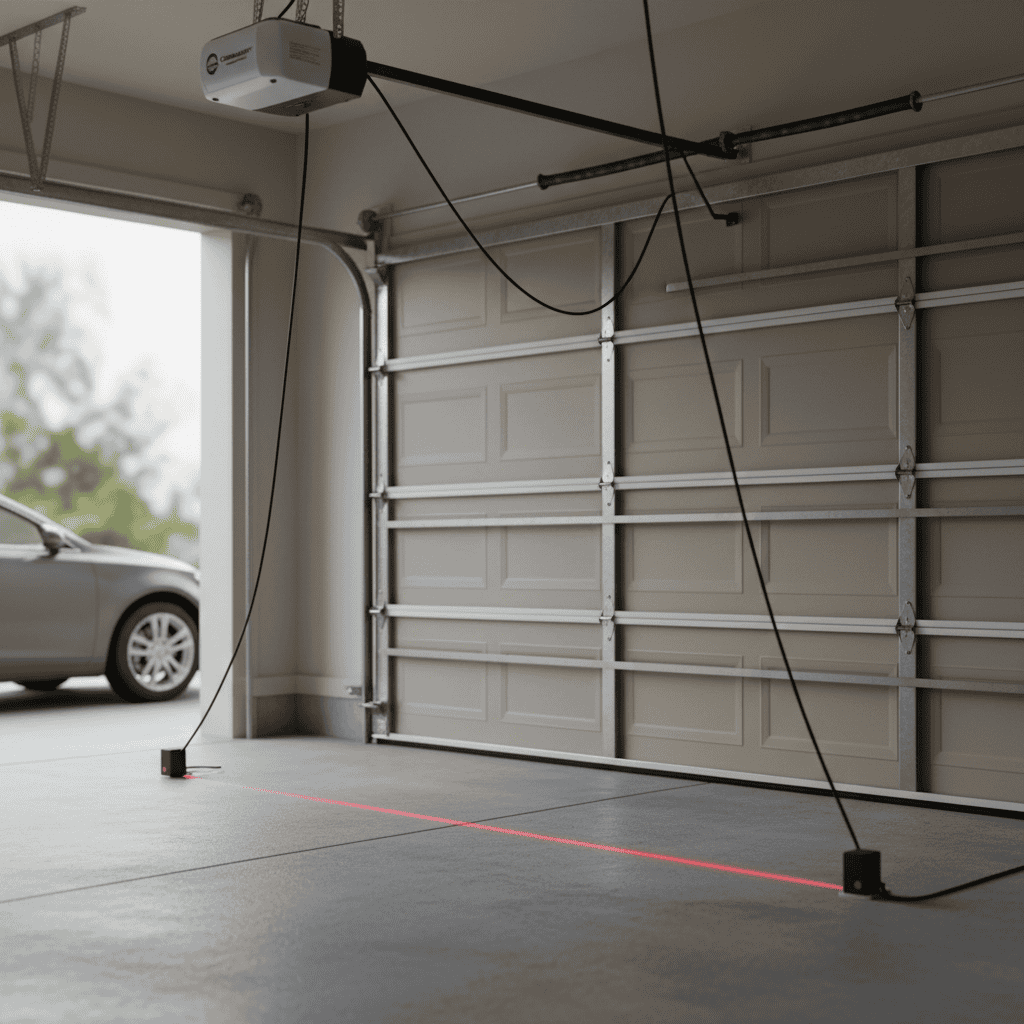
Safety Sensors and Photo Eye Technology Integration
Federal regulations mandate that all automatic garage door openers manufactured after 1993 include safety sensor systems preventing closure when obstructions are detected. These photo eye assemblies consist of an infrared sensor transmitter and receiver mounted on opposite sides of the door opening, approximately six inches above ground level. When the invisible beam is interrupted during closing cycles, the system immediately reverses door direction, preventing potential injury or property damage from entrapment situations.
Safety sensor problems represent one of the most common automatic garage door troubleshooting issues requiring professional attention. Photo eye misalignment caused by bumps, vibration, or mounting bracket shifts prevents proper beam transmission, resulting in garage door won’t close scenarios. Environmental factors including direct sunlight, dirt accumulation, spider webs, and condensation on sensor lenses can interfere with signal detection. Professional sensor alignment procedures ensure both units face each other precisely, with indicator lights confirming proper connectivity and beam integrity.
How Do Force Settings Affect Safety Sensor Operation?
Force settings calibration determines the amount of resistance required to trigger automatic door reversal during obstruction encounters. These adjustments work in conjunction with safety sensors to provide comprehensive protection against entrapment hazards. Limit switches control travel distance, signaling the motor when fully open or closed positions are reached. Improper force adjustment causes doors to reverse prematurely or fail to stop when encountering resistance, creating dangerous operational conditions.
Professional force settings calibration involves testing door response with deliberate obstructions placed in the path during closing cycles. The door should reverse immediately upon contacting a two-inch block placed on the ground. Technicians also verify that manually lifting a closing door requires no more than moderate resistance before automatic reversal engages. Travel module adjustments ensure doors open and close completely without overrunning limit positions or stopping short of proper sealing against weather stripping.
Garage Door Opener Systems and Secure Access Technology
The garage door opener market includes a variety of manufacturers and system designs, each offering different features and technology. Many modern opener systems use rolling-code security that generates a new access code with each use, helping reduce the risk of unauthorized entry attempts. Newer openers may also include built-in Wi-Fi connectivity that enables smartphone control through mobile apps and compatibility with popular smart home platforms.
Repair services commonly address smart connectivity issues, including app pairing, network connection problems, and device synchronization. Opener systems also offer various motor power options designed for different door weights and usage levels. Some models use battery-capable or backup-ready configurations to maintain limited operation during outages. Because hardware layouts and control panels vary by model, professional service ensures correct diagnosis, compatible replacement parts, and proper calibration after repairs.
Why Do Different Systems Require Specific Programming Procedures?
Manufacturers implement different programming protocols for remote control pairing, keypad programming, and in-vehicle system synchronization. These procedures typically involve specific button press sequences on wall controls, learn buttons on power units, and transmitter devices. Rolling-code security requires encrypted communication between transmitters and receivers, necessitating proper programming to establish secure connections. Older systems may use manual code settings, while modern units generally automate code and frequency selection to help minimize interference.
Professional garage door opener repair service includes programming remotes, keypads, and smart device applications according to system specifications. Technicians also account for compatibility limitations between components, since receivers and transmitters are not always interchangeable across different opener models. After power outages or circuit board replacement procedures, complete system reprogramming may be necessary to restore all remotes, keypad access codes, and vehicle connections to proper functionality.
Common Opener Problems and Troubleshooting Solutions
A garage door opener making a grinding noise typically indicates gear and sprocket wear within the motor housing assembly. This component bears significant stress during each operation cycle and may wear down over time. Gear replacement requires motor disassembly, removal of the old gear assembly, and installation of the correct replacement part. Clicking noises without door movement can indicate a failed capacitor, particularly in older units, preventing the motor from starting.
A humming motor without trolley movement may indicate a disconnected emergency release cord or internal drive mechanism failure. Belt slipping and loose chain conditions can cause intermittent operation or complete failure to engage the door. Proper chain tension and belt tension adjustments help ensure efficient power transfer from motor to trolley carriage. When a remote does not work but the wall button does, antenna positioning, receiver issues, programming, or transmitter battery replacement can often resolve the problem. Remote range issues may also result from interference caused by certain LED bulb types installed in opener light fixtures.
How Do Circuit Board and Logic Board Failures Present?
Circuit board failure can present as complete power loss, erratic operation, failure to respond to control inputs, or diagnostic LED patterns indicating errors. Logic board components control operational functions including travel limits, force settings, speed feedback, and safety sensor integration. Power surges, moisture exposure, and component age contribute to electronic deterioration requiring professional repair or replacement.
Capacitor testing determines whether this critical starting component maintains the electrical charge needed for motor initialization. Technicians use multimeters to measure capacitance values and compare readings against specifications. Circuit board replacement typically involves disconnecting terminals, documenting wiring locations, removing mounting hardware, and installing the correct replacement board. After installation, system reprogramming and force calibration restore proper operation and safety compliance.
Garage Door Springs, Cables, and Hardware Components
Garage door springs provide counterbalance force enabling motors to lift doors efficiently without excessive strain. Torsion springs mount on a shaft above the door opening, winding tightly during closing cycles and unwinding to assist opening. These high-tension components require professional handling due to significant stored energy and injury risk. Extension springs stretch along horizontal tracks on each side, expanding and contracting during operation cycles while connected to cables and pulleys.
Professional garage door maintenance includes spring inspection for wear indicators including gaps between coils, rust formation, and structural deformation. Cables connecting springs to door bottom brackets can fray, corrode, or break, causing dangerous unbalanced door conditions. Rollers, hinges, and tracks require lubrication and alignment verification ensuring smooth operation without binding or resistance. Track misalignment can cause binding, unusual noises, and premature component wear, while damaged rollers create excessive friction and strain on the opener.
What Maintenance Schedule Prevents Emergency Repairs?
Comprehensive preventative maintenance programs should occur semi-annually, addressing all mechanical, electrical, and safety components before failures develop. Inspection protocols include visual examination of moving parts and lubrication of rollers, hinges, springs, and tracks using garage-door-specific lubricants. Technicians test emergency release functionality, verify manual operation when power is disconnected, and confirm proper door balance so springs support the door’s weight without motor assistance.
Professional maintenance includes safety sensor testing to ensure photo eyes trigger immediate reversal during obstruction detection. Force settings receive testing and calibration adjustments to maintain compliance with safety standards. Hardware tightening addresses vibration-loosened mounting brackets, rail connections, and electrical terminals. Battery backup testing confirms emergency operation capability during power outages, particularly important for properties where garage access is a primary entry point. Documented maintenance history supports warranty needs and future troubleshooting.
Smart Home Integration and Wi-Fi Connectivity Features
Modern garage door automation may include smart home integration enabling remote monitoring, scheduling capabilities, and activity notifications through smartphone applications. Wi-Fi-enabled opener systems connect to home networks, allowing mobile app control from any location with internet access. These features can improve peace of mind through closure alerts, real-time status monitoring, and optional automation routines.
Smart opener setup requires stable wireless coverage in the garage, which may require range extenders or mesh networking in some homes. Security features often include encrypted communication protocols, user access logging, and guest access options that provide temporary entry without sharing permanent credentials.
How Does Battery Backup Ensure Continued Operation?
Battery backup systems help maintain functionality during power outages, preventing access disruption during emergencies or extended electrical interruptions. These systems use rechargeable batteries that remain charged during normal operation. When power loss is detected, the opener can switch to battery operation, typically providing a limited number of cycles depending on battery capacity and door weight.
Professional installation of battery backup systems includes proper electrical connection verification, initial charging procedures, and operational testing to confirm smooth transition between power sources. Status indicators may display charge levels and replacement alerts, as batteries commonly require replacement every three to five years depending on usage and conditions.
| Drive System Type | Noise Level | Maintenance Requirements | Average Cost Range | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain Drive | High | Periodic lubrication | $150-$250 | Detached garages |
| Belt Drive | Low | Minimal maintenance | $200-$350 | Attached garages |
| Screw Drive | Moderate | Low maintenance | $175-$300 | Moderate climates |
| Direct Drive | Very Low | Minimal maintenance | $300-$450 | Premium installations |
Professional Installation and Emergency Repair Services
Opener installation requires understanding of electrical wiring, structural mounting requirements, and safety compliance regulations. Professional technicians assess ceiling structure integrity, electrical power supply adequacy, and door compatibility before beginning installation. Mounting hardware must secure to structural supports capable of bearing operational loads, and rail installation must be properly aligned to prevent binding and premature wear.
Emergency garage door opener repair services address urgent situations including complete opener failure, doors stuck open compromising security, or safety hazards from damaged components. Repair costs vary based on required parts, labor complexity, and after-hours service needs. Professional repair includes diagnostics, approved replacement parts, and comprehensive testing to confirm restored functionality and safety compliance.
What Qualifications Should Professional Technicians Possess?
Qualified garage door service technicians should maintain proper licensing (where required), insurance coverage, and training demonstrating competency with multiple system types. Professional competency includes knowledge of electrical systems, mechanical drive mechanisms, safety sensor technology, and smart connectivity setup. Experienced technicians use specialized tools for force calibration and diagnostic equipment to identify electronic and mechanical failures.
Reputable service providers offer warranty coverage on parts and labor, transparent pricing, and prompt response times for routine and emergency service. Customer reviews, business ratings, and clear service policies can help indicate reliability. Professional technicians explain findings, present repair options when available, and recommend preventative maintenance practices that extend system longevity and reduce future repair frequency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I schedule professional garage door maintenance?
Professional maintenance should occur twice annually to inspect mechanical components, test safety sensors, lubricate moving parts, and verify proper force settings. Regular service helps prevent unexpected failures, extends component lifespan, and supports safety compliance. High-use commercial doors may require quarterly maintenance, while many residential systems benefit from spring and fall service visits.
Why does my garage door reverse immediately after closing?
Immediate reversal commonly indicates safety sensor misalignment, dirty photo eye lenses, track/roller resistance, or incorrect force settings. Ensure sensors face each other with indicator lights on, clean the lenses gently, and remove any obstructions. If the issue continues, professional force and travel calibration may be needed to restore safe operation.
What causes a garage door opener to hum but not move the door?
A humming motor without movement can indicate a failed capacitor, a disengaged trolley due to the emergency release being activated, or internal gear damage. Confirm the trolley is engaged. If the issue persists, professional inspection is recommended to test electrical components and verify mechanical integrity.
Can I replace a garage door opener myself or should I hire professionals?
Some homeowners can install an opener, but professional installation helps ensure correct electrical wiring, structural mounting, safety sensor alignment, and force calibration. Incorrect installation can create safety hazards, reduce performance, and affect warranty coverage. Professional installers also test safety features and confirm code-compliant operation.
How long do garage door openers typically last before replacement becomes necessary?
Many garage door openers last 10–15 years with proper maintenance, but lifespan varies based on usage, environment, and door balance. Signs replacement may be appropriate include frequent breakdowns, costly repairs, outdated safety features, excessive noise, or missing modern connectivity options.
What should I do if my garage door opener stops working during a power outage?
During an outage, pull the emergency release cord to disengage the opener and operate the door manually. Lift from the center using safe technique. If your opener includes a battery backup, it may continue operating for a limited number of cycles. After power returns, use the opener to re-engage the trolley and restore normal operation.